| Press Release |
August 7, 1997
New Media Development Association
| World's First ISO/IEC10536 Compatible
Contactless IC Card Was Developed For the Implementation of Electronic Commerce |
The New Media Development Association (NMDA) has developed a contactless IC card to be used in electronic commerce as part of the "Promotion of Electronic Commerce Projects" scheme funded by the Ministry of International Trade and Industry through the Information-technology Promotion Agency. This is the world's first contactless IC card compatible with the ISO/IEC10536 international standard (this is the international standard for up to 2mm close-coupling type IC cards).
1.Benefits of the Contactless IC Card
Various experiments have been carried out with electronic commerce throughout the country, using IC cards such as electronic cash. Most IC cards used in these experiments have external contacts on the surface of the card. To read and write data the terminal makes mechanical contact with the contacts on the card. Possible weak points of these cards include mechanical contact failure after repeated use of the card, electrical failure for personal identification cards, because they are kept over long periods, and problems with dust and moisture when using the cards outdoors.
Contactless IC cards, on the other hand, are free from these problems because they do not make mechanical contact, and offer the additional benefit of being useable in unfavorable environments where conventional IC cards cannot be used.
2.Development of the Contactless IC Card
In collaboration with the manufacturers of IC cards, the New Media Development Association has developed a technology for contactless IC cards to be used in electronic commerce as a part of the "Promotion of Electronic Commerce Projects" scheme funded by the Ministry of International Trade and Industry through the Information-technology Promotion Agency in order to solve the problems mentioned earlier. After verifying a prototype card in trials, the NMDA began to offer sample cards to the manufacturers of read/write devices for evaluation. The next step is to position this card as the next generation IC card for common usage in Japan by conducting validation tests and publicizing the technical specifications of the card.
The technical specification was developed in collaboration with Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd., Hitachi, Ltd., Denso Corp., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and Fuji Research Institute Corporation. In developing the IC card, Hitachi Ltd. worked on the IC chip and Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. took responsibility for developing the transmit/receive coils and the processing program ROM for the card system.
3.Features of the New IC Card
This is the first contactless IC card to meet the ISO/IEC10536 international standard (international standard for up to 2mm close-coupling type IC cards).
The main features of this IC card is its lack of contacts; data is transmitted by electromagnetic induction and is compatible with the software developed for the contact-type IC card (ISO/IEC7816 series), which is widely used. Regarding the encryption processing specified in the security section of the EMV specifications for international credit cards (EuroPay/ Master Card/ Visa Card), both the DES code (key length 64 bits) and the RSA code (key length 576 bits) can be used. Therefore, the card is expected to make a great contribution to the implementation of electronic commerce using IC cards as electronic cash.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
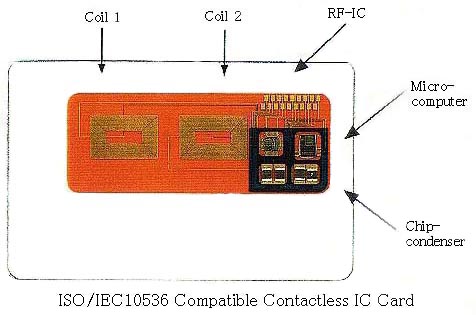
Structure of the Contactless IC Card
The following shows the structure of the close-coupling type contactless IC
card:
(See sample photo. Scale is about 1.4 times actual size.)
A) Coil 1, Coil 2
- The thickness of the copper foil is 35 microns, and each coil has 20
turns. The line thickness is 254 microns.
- A maximum electrical power of 150 mW is induced in the coils 1 and 2 by
the magnetic field generated by the reader/writer. Each coil sends and
receives data by electromagnetic induction.
B) RF-IC
- Commonly known as an analog circuit chip. The electrical power needed to
operate the microcomputer and the data communication signals are generated
in the coils by the induction field.
- This is the first RF-IC equipped with the functions required by the ISO
standard for frequency, level of electrical power, and communication method
(inductive data transmission).
C) Chip-condenser
- The chip-condenser provides a stable power source for the components on
the contactless IC card, i.e. the RF-IC and the microcomputer. The voltage
is 4.5 V for the RF-IC and 3.3V for the microcomputer.
D) Microcomputer
- The microcomputer consists of a CPU with advanced security functions and
an EEPROM (electrically erasable/programmable read only memory) to store
information. An arithmetic co-processor is added for speedy computation of
the encryption processes required for electronic cash and electronic
commerce. With the RSA public key encryption system it takes less than 1
second to calculate a 576-bit long key.
- ROM: 16 K bytes, RAM: 512 bytes, EEPROM: 8 K bytes
